Are you looking for a consistent income that will provide you with steady payments on a regulator basis? Then read on for a list of the top dividend paying stocks.
What is a Dividend?
A dividend is a payment made by a company to its shareholders. If you own a dividend paying stock you will generally receive a dividend in cash, but some companies will pay dividends in the form of shares.
The term dividend comes from the Latin term “dividendum” which means things to be divided. This refers to the company dividing a portion of its profits to their shareholders.
Dividends and capital appreciation are the primary methods of returning value to shareholders.
Why Do Companies Offer Dividends?
Most companies offer a dividend as a reward to their shareholders for purchasing and owning shares of their corporation. Recall, when a company issues public shares they are using the capital raise from distributed equity to enhance their operations and broaden their businesses.
A dividend is one of the ways a company entices investors to purchase their shares.
How Do Dividends Differ from Capital Appreciation?
There are generally two different ways that you can benefit from owning shares in a company. The first is that the price of the shares will rise, providing you with a capital gain.
The difference between where you purchased your shares and the current value is your unrealized gain. If you sell your shares, you have created a realized gain.
This differs from the income you will receive from a dividend payment.
When are Dividends Paid?
When you purchase a dividend paying stock you qualify to receive a dividend, based on specific eligibility requirements which are determined by the dividend dates. Dividend payouts are issued to investors on a per-share basis.
For example, if you purchase 10-shares of ABC stock that pays $0.50 per share, you will receive $5 in dividend payments (10-shares * $0.50). Generally, a dividend is deposited directly into your brokerage account.
Alternatively, if you purchase shares directly from a company through a direct investment plan, the dividends will be reinvested. This means that you will be using the payment to purchase more shares of the company.
You can also have dividends that are allocated through a direct investment paid via check.
How Often are Dividends Paid?
Most dividends distributed by a public company are paid quarterly. This means that you should expect to receive dividends four times a year. So, if company ABC pays an annual dividend of $1.00, you should expect to receive quarterly payments of $0.25.
Dividends are also paid semi-annually as well as annually.
Dividends that are issued to shareholders need to be approved by the Board of Directors of a company each time they are paid. However, holders of common stock are not necessarily guaranteed a dividend.
The company can simply choose not to pay any dividends. This will also take a Board of Directors vote. If you own shares of a company’s common stock and that company announces that it will pay a dividend to its shareholders, then you will receive the dividend.
Key Dates
There are three important dates the focus on dividend eligibility.
- Dividend Declaration Date
- Date of Record
- Ex-dividend Date
- Payment Date
The dividend declaration date is the date that the Board of Directors announces its intention to pay a dividend.
The date of record is the date on which the investor must own the shares and be on the company’s books in order to receive a dividend.
The ex-dividend date is the first date that the company is not trading with the value of a dividend. The record date is often confused with the ex-dividend date. Recall that the record date is set by the company. The ex-dividend date is set by the stock exchange. The ex-dividend date is generally a few dates earlier than the record date due to the settlement period for stock trades on exchanges.
The payment date is the date the dividend is transferred to the shareholders.
Example of a Dividend Payment
If you plan to purchase shares with a goal of receiving dividends as income you want to have a clear understanding of the process. Here is an example of how a dividend payment would work if you owned 100-shares of Disney beginning on December 1, 2019. Disney pays is dividends semi-annually.
On December 4, 2019, the Board of Directors of Disney Corporation announced a dividend payment of $0.88 per share payable to shareholders on January 16, 2020.
To be eligible to receive the dividend, you most own the shares on the close of business on December 16, 2019.
You cannot sell the shares on or before that date and still receive the dividend. On January 16, 2020, a cash payment of $88 would have been deposited into your brokerage account.
What Is Dividend Reinvestment?
Dividend reinvestment is the process of buying more shares with the dividend you receive. There are two ways you can reinvest using your dividend. You can take cash and then at your leisure purchase more shares.
Alternatively, you can automatically purchase more shares with the dividend payment. There are several benefits of automatic reinvestment.
- Cost Effective. You will not owe any commissions or brokerage fees when you automatically reinvest in shares.
- Easy and efficient. Once you set it up, dividend reinvestment is automatic.
- You can buy fractional shares with dividend reinvestment.
- Consistent Investing. You are buying shares on a regular basis.
One of the benefits of dividend reinvestment is compounding. This allows you to enhance your returns and grow your wealth. Compounding is the process in which an asset’s earnings, are reinvested to generate additional earnings over time.
This growth rate of your earnings is calculated using exponential functions because the investment will generate earnings from both its initial principal and the and the dividend reinvestment from preceding periods.
Here is an example:
Company XYZ pays a dividend of $2 per year annually one time at the end of the year. Let’s assume that you purchase 100-shares of the stock at the price of $20 per share.
We will also assume that the stock prices rise by 5% each year for the next 5-years. Your initial investment when you purchase the shares is $2,000.
After the first year, you will receive $2 in dividend payments when the price of the stock is $21 ($20 * 1.05). You will be able to reinvest your $200 dividend ($2 *100-shares) to purchase 9.5-shares of XYZ stock ($200 / $21). Recall, a dividend reinvestment plan generally allows you to purchase fractional shares.
At the beginning of year 2, you own 109.5 shares that are worth $2,300. At the end of year two, the share price rises to $22.05, and you would receive another dividend payment.
The dividend would be based on 109.5 shares as opposed to 100-shares which was your initial investment. Your dividend payment would then be $219 (109.5 * $2), assuming a $2 dividend payment.
With the price of the shares at $22.05, you would reinvest your dividend and receive another 9.9 shares. This would put the total number of shares you own at 119.4.
The value of your shares would then be 119.4 * the current price of $22.05, making the value of your investment $2,632.
If you did not reinvest your dividend, the value of your shares would be $2,605, allowing you to generate an additional $27 from reinvestment over 2-years.
Stocks or ETF Dividends?
Whether you are looking to reinvest your dividends or use the cash for another purpose, you can generate income from dividends through stocks as well as exchange traded funds (ETFs).
EFT is generally used to track an index, but many own individual stocks that pay dividends to the fund. When this occurs the fund manager collects the regular dividend payments and then distributes them to the ETF shareholders.
The dividends are distributed at the discretion of the fund’s management. They might be paid in cash or reinvested into the ETFs’ underlying investments.
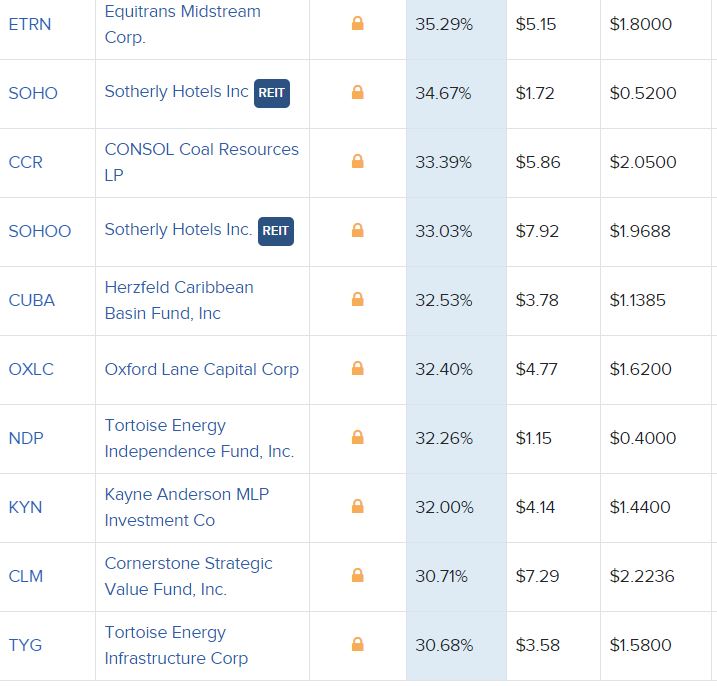
Top 20-Dividend Paying Stocks and ETFs
Once of the best ways to analyze the value of a dividend is through the dividend yield. This is the annual dividend that a company has historically paid, divided by the current price.
Here are the top 20-dividend yielding stocks and ETFs.
Bottom Line
Dividends are a great way to earn income while investing in stocks. Not only can you receive a cash payment that enhances your return, but you can also reinvest the dividends you receive and compound your investment returns.
Dividends are payments from a company to investors to entice investors to purchase shares. Dividends are generally paid quarterly, to the holder of record. Dividends can also be paid semi-annually or annually.
Before dividends can be paid, it needs to be approved by the Board of Directors of a company.
There are several ways to evaluate a dividend. You want to make sure that a company has a track record of consistently paying a dividend. Since the dividend is not guaranteed, you need to understand that there is a reason some companies have a high dividend yield.
If you do your homework you can find several dividends paying companies that will provide you with steady income through both capital gains and dividend income.